Cardiovascular disease
Do you feel pain in the left side of the chest? If yes then you must have some problems in your heart. Now there have different problems in heart. 17.9 million people die each year throughout the world due to heart disease according to WHO (World Health Organisation). Turkmenistan saw the highest rate of deaths from cardiovascular disease in 2012, with 712 deaths per 100,000 people. At least 48 percent of all adults in the United States have some form of cardiovascular disease, according to the latest statistics. So it is high time we should keep a check on our heart. So lets just see how can we avoid heart disease.
What is cardiovascular disease ?
Cardiovascular disease is a broad term
comprising of a spectrum of diseases associated with disorders of the heart and
blood vessels, circulation and associated functions. The major forms include
dyslipidaemia, atherosclerosis, hypertension, angina pectoris, myocardial
infaction, congestive cardiac failure and rheumatic heart disease.
Common disorders and complications of Coronary
Heart Disease:
1. Dyslipidemia:
2. Atherosclerosis:
3. Hypertension:
Higher than normal blood pressure.
4. Angina pectoris:
A characteristics pain or discomfort in the
chest.
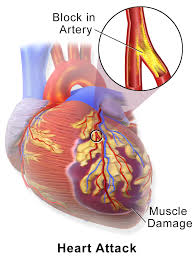
5. Myocardial Infarction:
An area of necrosis (dying/dead cells
of the myocardium) in a tissue.
6. Congestive Cardiac Failure (CCF):
A clinical syndrome caused
by heart disease characterized by breathlessness, chest pain and abnormal
sodium and water retention.
7. Rheumatoid Heart Disease:
A complication of rheumatic fever
and occurs after attacks of this fever.
Causes of heart Diseases: The factors that play a role in causing or
increasing the risk of getting cardiovascular disease are called the risk
factors. Risk factors may be of two types:
· Modified Risk factors: These factors are changeable i.e. you can change the factor causing the heart disease.
1. Behavioural: This factors depends upon your behavior which can be modified. Such as Smoking, sedentary lifestylehabbits and dietary errors.
Ø Smoking: Smoking is a most important cause of cardiovascular disease. When you smoke, nicotine enters into the body. As you know nicotine is a life killing a highly addictive chemical compound which increases blood pressure, heart rate and flow of blood to the heart and makes the arteries narrow. This also cause irregular heart rhythm and makes the arterial walls hardens. This makes the heart work harder and leads to heart attack.
Ø Sedentary Lifestyle Habits: When you lead a sedentary lifestyle it increases the chance of developing heart disease more than 30-50 percent. AS this increases your blood pressure. Moreover when you have a inactive life, the fatty materials from your body starts building up in the arteries that carry blood to your heart. This damages and clogged the arteries which can lead to heart attack.
Ø Dietary Errors: Diet is an important role of causing heart disease. A wrong disease can obesity, a risk factor for heart disorders. This can also cause high blood pressure and uncontrollable diabetes, which increases the risk of heart diseases. Diet containing low saturated fats, high fibre and high plant food can reduce the chance of developing heart disease.
2. Physiological: The biological factors that are responsible for heart disease. That includes hyperlipidemia, hypertension, obesity, diabetes mellitus, hyperuricemia and gout, fibrinogen, platelet aggregation, lipoprotein, homocysteine levels, low birth weight.
Ø Hyperlipidemia: This is a condition where your body contains high amount of lipid i.e. cholesterol and triglycerides. These lipids gets deposited into the walls of blood vessels and restrict blood flow to the heart. This increases the risk of heart attack and stroke. This doesn’t show any symptoms. This is diagnosed by routine blood test which is recommended each year for the adults.
Ø Hypertension: This condition occurs when blood pressure against the artery wall becomes high. At this time the blood pressure remains 140/90. But this becomes serious when blood pressure becomes 180/120. This also have no symptoms but if it is left untreated then it can lead to heart attack and stroke.
Ø Obesity: This is a state which included accumulation of excessive fat resulting from high calorie consumption than burning. This increases the risk of heart attack.
Ø Diabetes Mellitus: This is a metabolic disease that causes high blood sugar. These high blood sugar damages the blood vessels and nerve that controls the heart. This increases the risk of heart disease.
Ø Hyperuricemia and Gout: Hyperuricemia is a disease which is caused due to high uric acid. These then settle in the bone joints causing gout. Gout is the disease of inflammation in the joints. This may cause pain in toe but it can affect other organs including the heart.
Ø Fibrinogen: It is a glycoprotein complex formed in the liver and circulates in the blood. During any injury this fibrinogen is converted to fibrin and then to fibrin based blood clot by thrombin which stops the blood vessels from bleeding. Low fibrinogen levels can also cause thrombosis due to an increase in coagulation activity. Thrombosis refers to the formation of a blood clot inside of a blood vessel. The clot blocks the normal flow of blood through the circulatory system. This can lead to serious medical conditions such as heart attack and stroke according to healthline.
Ø Platelet Aggregation:This is a part of series of events in the blood which forms thrombus. During the platelet aggregation a product is released which cause atrial spasm. So people having chance of coronary heart disease they are found to have abnormally reactive platelets.
Ø Lipoproteins: Lipoproteins of low density sends cholesterol to the cells of the artery walls causing artery clogging plaque which increases the risk of heart attack.
Ø Homocysteine Levels: High level of homocysteine levels damages the lining of arteries cause blood clot more easily. This increases blood vessel blockage leading to heart attack.
Ø low birth weight: Children having low birth weight are known to have low amount of good cholesterol and high bad cholesterol. All these factors increase the chance heart diseases.
1. Psychological: There are many psychological factors that plays an important role in developing heart diseases. Such as stress.
Ø Stress: When you have a long term of stress it increases the level of cortisol, which increases blood cholesterol, triglycerides, blood sugar, blood pressure, the risk factors of heart attack.
· Non-modified risk factors: These factors are not changeable by an individual.
1. Age: As you grow older the risk of heart attack increases. The average age of heart attack for man is 65 and for women is 70. About 20% of people who die due to heart attack is under 65.
2. Sex: Mens are at higher risk of developing heart diseases than women.
3. Hereditary: Hereditary is one of the most important risk factors for developing heart disease in men who under 55 years and in women 65 years. And cardiovascular diseases in an individuals parents increases their risk by 3 folds.
Symptoms of cardiovascular diseases:
·
pain or pressure in
the chest, which may indicate angina.
·
pain or discomfort in
the arms, left shoulder, elbows, jaw, or back.
·
shortness of breath.
·
nausea and fatigue.
·
lightheadedness or
dizziness.
·
cold sweats.
Mechanism of
developing of heart disease:
· Improper diet, unhealthy lifestyle and genetic predisposition can together lead to faulty lipid profile or dyslipidemia.
· Due to this, lipid may accumulate in the blood vessels, leading to atherosclerosis, as a result of which blood vessels are narrowed.
· For blood to flow through this narrow vessels, more pressure develops, a condition known as hypertension.
· During atherosclerosis, the platelet of the blood comes in contact with the uneven walls of the blood vessels and is broken down forming blood clot.
· Due to atherosclerosis, sufficient blood may not reach the important part of the heart, causing ischaemia (reduced o2 and food in cardiac circle).
· Prolonged ischaemia can cause damage to particular area which may cause pain and discomfort, a condition referred to as angina pectoris.
· Permanent damage to the heart cells leading to improper functioning can lead to myocardial infarction or heart failure.
Management:
1. Dietary management: The goals of dietary management are to reduce the total fat, saturated fat and cholesterol intake to maintain normal body weight. The following are some dietary principles that can be followed-
· Calories: The total calorie should be planned in such a way so that it can help to maintain ideal body weight.
· Carbohydrates: Carbohydrates should provide about 60-70% of the total calorie needs of the body. If taken in excess the extra calorie can be converted to fat in the body. Generally complex polysaccharide should be suggested and simple carbohydrates and high GI good should be avoided.
· Protein: While the quantity of the protein does not impose any significant impact on the serum lipoprotein, it is quality of protein, which may be significance. Patients should be advised to consume plant origin protein over those of animal origin about 0.8-1 gm/kg ideal body weight.
· Fats: Fat should be avoided or restricted. Not more than 20 % of the total calorie should be given. Saturated fatty acid and cholesterol rich food should be avoided. MUFA, PUFA having cholesterol lowering and blood pressure lowering should be included into the diet.
MUFA and PUFA have a plasma cholesterol lowering effect. Omega-3-fatty acids are excellent for the heart as they-
Ø Reduce platelet aggregation and monocyte adherence
Ø Modify plasma lipids
Ø Lower blood pressure
· Minerals: The three most important minerals are chromium, zinc and magnesium. Excess sodium intake and lack of potassium is also significant in causing heart disease.
· Vitamins: Antioxidant vitamins like vitamin E, A and C can scavenge cell-damaging free radicals, which may lead to various types of heart diseases. Multivitamin tablet should be given containing water soluble vitamin.
· Fiber: Fibre is beneficial for cardiovascular disease. Soluble fiber like pectins, gums and mucilages have shown reduction in cholesterol levels. Soyabean is good source of fibre and soya proteins have oestrogenic effect, which cause lipid lowering.Lecithin fat reduces cholesterol level.
Dietary guidelines by WHO:
· Calorie should be given to maintain ideal body weight.
· Carbohydrate should constitute 55-65% of calories with emphasis of polysaccharides (complex carbohydrates)
· Sugar should be less than 10% of the total calories.
· Proteins should provide about 15-20% of the modified calories.
· Fats should be less than 10-15% of the total energy.
· Cholesterol intake should be reduced.
· Refined and processed products should be avoided.
· Fresh fruits should be consumed.
· Organ meats ( brain, liver, kidney ), high salt-containing foods, whole milk and its products should be avoided.
· Dietary modifications should be individualized.
· Fluid restriction is necessary only if oedema is present.
2. Other management Techniques:
· Lifestyle changes: Smoking, use of tobacco, excess alcohol intake should be avoided. Physical activity like walking, cycling, swimming, etc. may be beneficial.
· Medications: Diuretics and other medicines, if prescribed by the doctor should consumed.
DASH Diet is now followed for treating heart disease patients. Adopt Dietary Approach to Stop Hypertension is DASH Diet. It encourages the consumption of diet rich in fruits and vegetables low in sodium content and low fat dietary products with reduced content of saturated and total fat.







Comments
Post a Comment
if you have any dobt , let me know